Written by Don Richardson
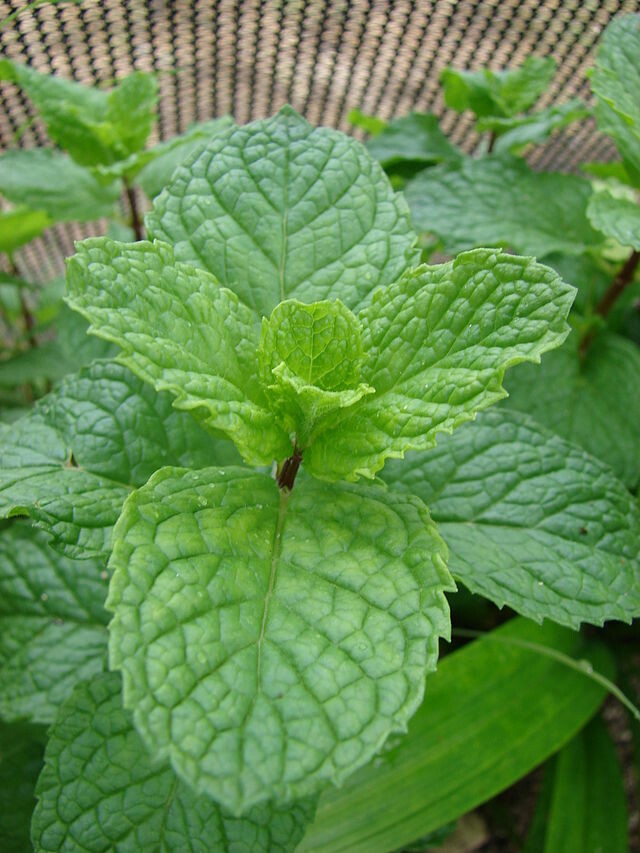


Mint (Mentha Spicata) 'Spearmint'
Plant Type | Perennial Herb/Ground Cover |
Size | 1-3’ tall, 1-2’ wide, spreads |
Sun Exposure | Full sun – part shade (3hrs.+) |
Soil Type | Light sand, loam, clay |
Soil pH | 6.0-7.0 acidic - alkaline |
Bloom Time | Summer - Fall |
Hardiness Zones | 3a-10 Food Forest Plant |
Moisture | Moist, well drained |
Cold/Heat | -30°F – |
Pollination | Self-pollinates, self-seeds |
Edible Plant | Yes |
Medicinal Plant | Yes |
Any reference to medicinal or culinary use of plants or plant parts should in no way be considered an endorsement by The Ocala Food Forest or its staff. Research is crucial in safe and proper consumption or experimentational use of any plant.
The Mentha spicata, more commonly known as the spearmint plant, is a species of mint that has a long history of medicinal and culinary uses. It is native to Europe and Asia, but it can now be found in many parts of the world. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at this versatile plant and explore its many benefits.
History and Origin of the Spearmint Plant
The spearmint plant has been used for thousands of years for its medicinal properties. Ancient Greek and Roman cultures both used spearmint as an herbal remedy for a variety of ailments, including digestive issues and headaches. The plant was even mentioned in ancient texts such as Theophrastus’ Historia Plantarum, written in 300 BC.
Description
The Spearmint plant grows up to 30-90 cm tall and has greenish or reddish stems with serrated oval leaves. The leaves can be either opposite or in whorls of three, while the flowers are usually pink or lilac in color. It thrives best in moist soils but can survive in most soil types. It also requires plenty of sunlight and will begin to flower between mid-summer and late summer when temperatures remain consistently warm.
Culinary Uses
The oil from the leaves of the Spearmint plant is widely used as a flavoring agent in many culinary applications such as candy, gum, ice cream, toothpaste, tea, liqueurs and sauces. While it shares some flavor notes with peppermint (Mentha Piperita), it has a much sweeter taste than its close cousin due to lower concentrations of menthol. For that reason, spearmint is often favored by people who may find peppermint too overpowering for their tastes.
Medicinal Properties
Spearmint has been used medicinally since ancient times and is believed to have many health benefits including aiding in digestion, reducing muscle spasms, relieving headaches and congestion, treating skin irritations and improving oral health. In addition, it contains high amounts of vitamin A which helps promote healthy skin growth as well as antioxidants which helps fight against free radicals that damage cells over time. Finally, research suggests that consuming spearmint tea regularly may help reduce levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) while raising levels of good cholesterol (HDL). It can also be made into essential oil that can be added to bath water or massaged into the skin for relaxation purposes.
Conclusions:
All in all, the Spearmint plant provides not just flavorful culinary experiences but also much needed medicinal properties for our overall well-being too! Whether you’re looking for a unique way to liven up your dishes or want a natural remedy for common ailments like headaches and digestion issues - look no further than the humble Spearmint plant! With proper care this versatile species can provide you with plenty of delicious flavors and therapeutic benefits for years to come!
All in all, the Spearmint plant provides not just flavorful culinary experiences but also much needed medicinal properties for our overall well-being too! Whether you’re looking for a unique way to liven up your dishes or want a natural remedy for common ailments like headaches and digestion issues - look no further than the humble Spearmint plant! With proper care this versatile species can provide you with plenty of delicious flavors and therapeutic benefits for years to come!








0 Comments