Written by Don Richardson
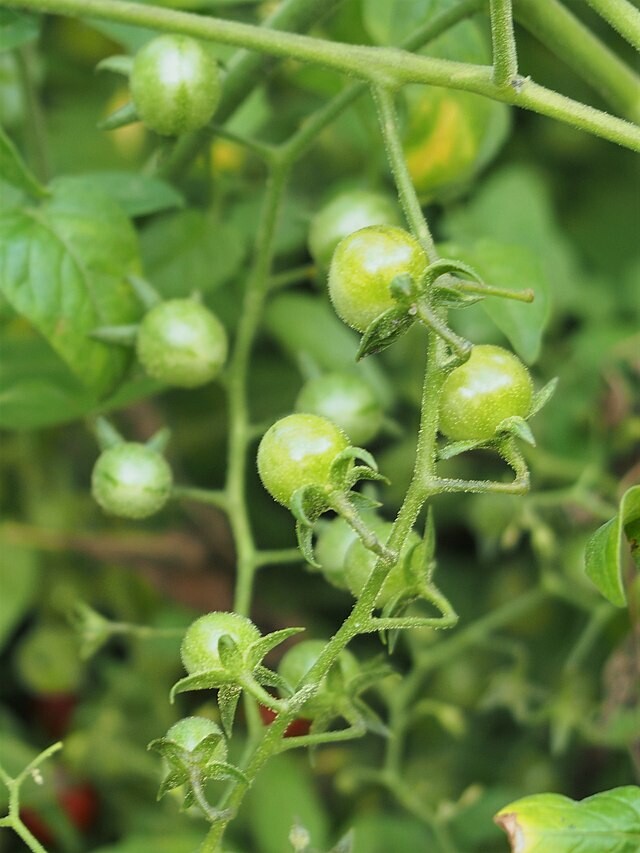
 Everglades Tomato (Solanum pimpinellifolium)
Everglades Tomato (Solanum pimpinellifolium)Plant Type | Annual/Biennial Fruit |
Size | Up to 6’ tall |
Sun Exposure | Full Sun |
Soil Type | |
Soil pH | |
Bloom Time | Most all year |
Hardiness Zones | 10 - 11 Food Forest Plant |
Moisture | Moderate, drought tolerant |
Cold/Heat | 40°F – |
Pollination | Self-pollinates |
Edible Plant | Yes |
Medicinal Plant | Yes |
Any reference to medicinal or culinary use of plants or plant parts should in no way be considered an endorsement by The Ocala Food Forest or its staff. Research is crucial in safe and proper consumption or experimentational use of any plant.
The Everglades tomato, or Solanum pimpinellifolium, is a plant native to the Florida Everglades. It is an important source of nutrition for native wildlife and humans alike. This article will provide an overview of this unique species, discussing its characteristics and benefits.
Characteristics
The Everglades tomato is a shrub-like plant with long stems that can reach heights of up to 3 feet tall, but can reach heights up to 6 feet in optimal conditions. Its leaves are smooth and oval shaped, with a glossy green color. The small yellow flowers have five petals each and are clustered around the stem in groups of two to three. These flowers produce small cherry-sized tomatoes that can be eaten raw or cooked into sauces and other dishes.
The Everglades tomato is adapted to grow in wet conditions, making it well suited for the warm and humid climate in South Florida’s wetlands. It prefers full sun exposure but can also survive in partial shade. It has strong roots that help it survive floods or periods of drought by storing water for later use. Additionally, it can survive in soil with low levels of fertility since it does not require many nutrients from the environment to thrive.
Benefits of Eating
The Everglades tomato is high in vitamins A, C, B6, folate, potassium, calcium and magnesium as well as dietary fiber which makes them beneficial for human health when eaten raw or cooked into sauces or other dishes. They have been used as a traditional medicine among indigenous populations in Florida for centuries due to their anti-inflammatory properties which may help reduce pain and swelling caused by rheumatoid arthritis or other joint conditions. Additionally, they contain lycopene which helps protect against certain types of cancer such as prostate cancer and may reduce cholesterol levels when consumed regularly over time. Furthermore, they contain antioxidants like beta carotene which helps reduce free radical damage caused by oxidative stress in our bodies due to exposure to environmental toxins such as air pollution and cigarette smoke.
For wildlife, the berries are an important food source for songbirds, waterfowl, raccoons, opossums, deer, foxes, bobcats and rabbits during certain times of year when other food sources may be scarce. Furthermore, pollinators like bees use it as a nectar source for honey production. Finally, it serves as a host plant for several butterfly species including zebra longwings (Heliconius charithonia) and giant swallowtails (Papilio cresphontes).
Conclusion:
The Solanum pimpinellifolium (Everglades Tomato) is an important plant species found only in South Florida's wetlands region known as the Everglades National Park. It is a nutritionally dense food that contains vitamins A, C & B6; folate; calcium & magnesium; dietary fiber & antioxidants; plus anti-inflammatory & cholesterol lowering properties when consumed regularly over time — making them beneficial for both humans & wildlife alike! Not only do these plants have culinary uses but they also provide valuable habitat for birds & other animals living in the park’s ecosystem — helping to maintain its health & diversity! For those looking for delicious local produce or interested in learning more about this unique native species – be sure to check out your local farmers market today!
The Solanum pimpinellifolium (Everglades Tomato) is an important plant species found only in South Florida's wetlands region known as the Everglades National Park. It is a nutritionally dense food that contains vitamins A, C & B6; folate; calcium & magnesium; dietary fiber & antioxidants; plus anti-inflammatory & cholesterol lowering properties when consumed regularly over time — making them beneficial for both humans & wildlife alike! Not only do these plants have culinary uses but they also provide valuable habitat for birds & other animals living in the park’s ecosystem — helping to maintain its health & diversity! For those looking for delicious local produce or interested in learning more about this unique native species – be sure to check out your local farmers market today!








0 Comments