Written by Don Richardson
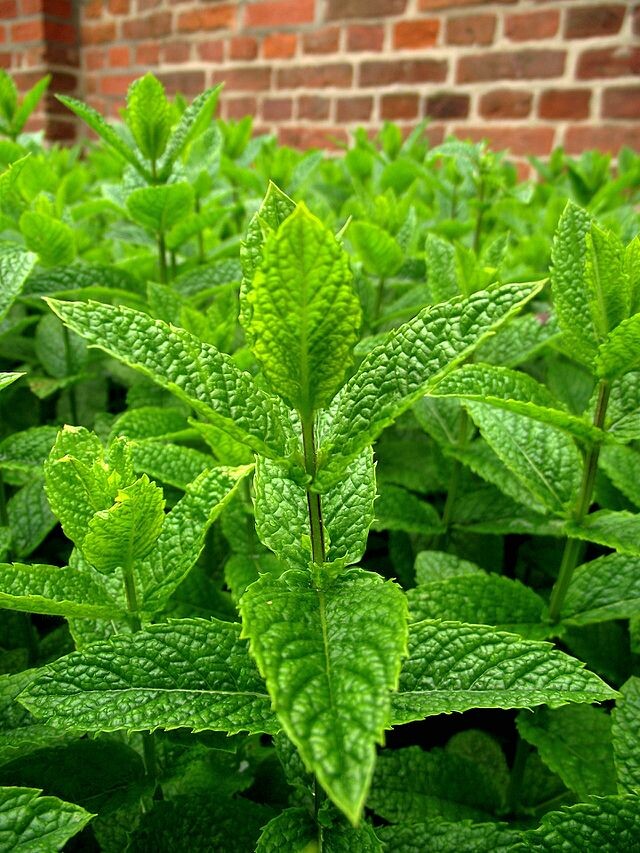
 Mint (Mentha x Piperita) 'Chocolate'
Mint (Mentha x Piperita) 'Chocolate'Plant Type | Perennial Herb/Ground Cover |
Size | 1-3’ tall, 1-2’ wide, spreads |
Sun Exposure | Full sun – part shade (3hrs.+) |
Soil Type | Light sand, loam, clay |
Soil pH | 6.0-7.0 acidic - alkaline |
Bloom Time | Spring & Summer |
Hardiness Zones | 3a-10 Food Forest Plant |
Moisture | Moist, well drained |
Cold/Heat | -30°F – |
Pollination | Self-pollinates, self-seeds |
Edible Plant | Yes |
Medicinal Plant | Yes |
Any reference to medicinal or culinary use of plants or plant parts should in no way be considered an endorsement by The Ocala Food Forest or its staff. Research is crucial in safe and proper consumption or experimentational use of any plant.
The chocolate mint plant (Mentha x Piperita) is a hybrid of watermint and spearmint that grows wild in many parts of the world. With its distinctive aroma and flavor, it has been used for centuries to make all kinds of culinary delights. This blog post will delve into the world of this unique herb, exploring its history, uses, varieties, and more.
History and Origins
The exact origin of the chocolate mint plant is unknown; however, it likely originated in Europe where it was cultivated by ancient Greeks and Romans. In the 18th century, it was introduced to North America by European settlers who brought it with them as they colonized new lands. Today, it grows wild throughout much of the temperate regions of Europe and North America.
Types Of Chocolate Mint Plant
There are several varieties of Mentha x Piperita that vary in their appearance and flavor profiles. One common variety is known as “orange” or “citrus” mint which has a stronger citrusy flavor than other varieties. Another common variety is called “black” or “smokey” mint which has a smokier taste than other types due to its higher concentration of oils. There are also peppermint-scented versions which have a sharper menthol scent than other types.
Uses Of Chocolate Mint Plant
The chocolate mint plant is most commonly used for culinary purposes but can also be used medicinally or even ornamental purposes. In terms of cooking, its leaves can be used fresh or dried in order to add flavor to dishes such as salads, teas, sauces, desserts, and much more. It can also be utilized as an herbal remedy; when brewed into a tea or tincture it can help alleviate indigestion and stimulate circulation. Finally, its beautiful bright green foliage makes it an attractive addition to any garden landscape!
Conclusion:
Chocolate mint plants have been prized for centuries for their aromatic leaves that can add an extra zing to many dishes or drinks - from teas to salads! Not only that but they can also be used medicinally or even just enjoyed as part of your garden landscape due to their attractive foliage! Whether you want to use them for cooking or just appreciate them aesthetically - there's something for everyone when it comes to this versatile plant! So why not give chocolate mint plants a try? You won't regret it!
Chocolate mint plants have been prized for centuries for their aromatic leaves that can add an extra zing to many dishes or drinks - from teas to salads! Not only that but they can also be used medicinally or even just enjoyed as part of your garden landscape due to their attractive foliage! Whether you want to use them for cooking or just appreciate them aesthetically - there's something for everyone when it comes to this versatile plant! So why not give chocolate mint plants a try? You won't regret it!
Written by Don Richardson
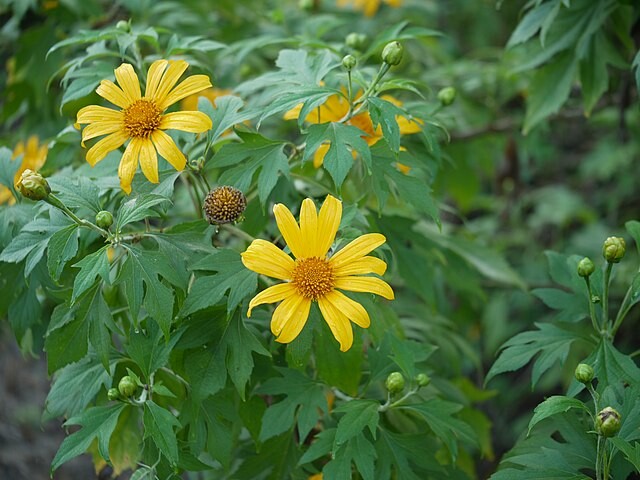
 Mexican Sunflower (Tithonia Diversifolia)
Mexican Sunflower (Tithonia Diversifolia)Plant Type | Perennial Shrub |
Size | 10’ tall, 3’ wide, spreads |
Sun Exposure | Full sun |
Soil Type | Light sand, loam, clay |
Soil pH | 5.6-7.8 acidic - alkaline |
Bloom Time | Summer, Fall, Winter |
Hardiness Zones | 9b-11 Food Forest Plant |
Moisture | Moderate Water, well drained |
Cold/Heat | 25°F – 110°F, Drought tolerant |
Pollination | Pollinator, self-seeds |
Edible Plant | No |
Medicinal Plant | Yes |
Any reference to medicinal or culinary use of plants or plant parts should in no way be considered an endorsement by The Ocala Food Forest or its staff. Research is crucial in safe and proper consumption or experimentational use of any plant.
The Tithonia Diversifolia is a vibrant, eye-catching plant that grows in tropical regions. It is commonly known as the Mexican Sunflower, and it has become increasingly popular among gardeners in recent years. Let’s explore what makes this plant so special and why you should consider adding it to your own flower bed!
The Basics of Tithonia Diversifolia
Tithonia Diversifolia is native to Mexico, Central America, and parts of South America. It belongs to the Asteraceae family and can reach heights of up to 10 feet tall with flowers in shades of yellow, orange, and red. This plant can thrive in almost any soil type as long as it receives ample sunlight. It requires very little maintenance; all it needs is regular watering and occasional pruning for optimal growth.
In addition to its aesthetic appeal, the Mexican Sunflower has practical benefits too. It attracts beneficial insects such as bees which help pollinate other plants in your garden; plus, its strong stems make it an ideal windbreak for other plants that may be more fragile. The plant also produces a high amount of nectar which makes it attractive to birds as well. By planting by plants that are affected by aphids or many other insects, the birds will take care of many insects invading your garden.
Uses for Tithonia Diversifolia
Tithonia Diversifolia has many uses beyond just decorating your flower bed. Its flowers can be used to make tea or dried for use in potpourri; even the stems are useful because they can be made into rope or woven baskets! Additionally, some herbalists believe that this plant has medicinal properties due to its high content of Vitamin A and antioxidants.
Conclusion:
All in all, Tithonia Diversifolia is an ideal addition to any garden since not only does it provide a beautiful display but also several practical uses too! With its vibrant colors and low-maintenance care requirements, this plant is sure to brighten up your outdoor space while providing a variety of benefits for both you and your garden guests alike! Whether you’re looking for something decorative or functional (or both!), Tithonia Diversifolia is worth considering when planning your next gardening project.
All in all, Tithonia Diversifolia is an ideal addition to any garden since not only does it provide a beautiful display but also several practical uses too! With its vibrant colors and low-maintenance care requirements, this plant is sure to brighten up your outdoor space while providing a variety of benefits for both you and your garden guests alike! Whether you’re looking for something decorative or functional (or both!), Tithonia Diversifolia is worth considering when planning your next gardening project.
Written by Don Richardson
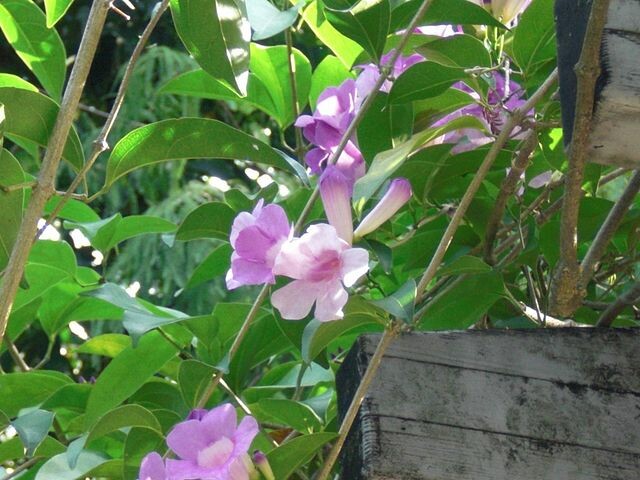
 Garlic Vine (mansoa hymenaea)
Garlic Vine (mansoa hymenaea)Plant Type | Perennial Vine |
Size | 6-8’ long |
Sun Exposure | Full sun |
Soil Type | All soil types |
Soil pH | 5.0-6.5 slightly acidic - alkaline |
Bloom Time | Spring & Fall |
Hardiness Zones | 8b-11 Food Forest Plant |
Moisture | Moderate Water, well drained |
Cold/Heat | 34°F – Drought tolerant |
Pollination | Self Pollination |
Edible Plant | Yes (entire plant is edible) |
Medicinal Plant | Yes |
Any reference to medicinal or culinary use of plants or plant parts should in no way be considered an endorsement by The Ocala Food Forest or its staff. Research is crucial in safe and proper consumption or experimentational use of any plant.
The mansoa hymenaea, known more commonly as the garlic vine plant, is a species of liana native to tropical and subtropical parts of Central America. It can be found in rainforests and evergreen forests from Mexico south to Brazil. This woody vine is highly appreciated for its ornamental value, thanks to its fragrant flowers and edible fruits. It is popularly cultivated for its fragrant flowers and pungent foliage. In addition to its ornamental value, it has also been used in traditional medicine for its various medicinal properties. Let’s take a closer look at this woody vine and learn more about it.
Identification of the Mansoa Hymenaea Plant
The garlic vine plant typically grows white or violet color flowers and have a spicy garlic-like aroma that’s particularly prominent at night. The fruit of this plant is an edible berry that’s yellow-orange when ripe and contains small, hard seeds. The leaves are entire and glossy, with a leathery texture on the upper side. They have an unmistakable smell of garlic when touched or crushed.
Uses and Benefits of Garlic Vine
This species is popularly used as an ornamental plant due to its pleasing appearance and distinctive smell. Its berries are also edible, although they are not widely consumed because of their bitter taste when unripe. The garlic vine plant has been traditionally used as a culinary herb due to its pungent flavor and aroma. Its leaves are sometimes added to salads or cooked dishes to provide an extra kick of flavor. In addition, this plant produces nectar which attracts different kinds of wildlife such as birds and butterflies into gardens where it grows wild. Furthermore, this species of liana has also been used in traditional medicine for various medicinal purposes such as treating infections caused by bacteria and fungus as well as providing relief from pain and inflammation. Its bark has been used medicinally for many years by some Amerindian groups for treating skin ailments such as eczema or wound healing issues like sores or abscesses.
Cultivation & Care Instructions
The garlic vine plant is easy to grow provided you follow some simple care instructions such as providing sufficient sunlight (at least 6 hours per day). The plant prefers temperatures between 65°F – 77°F, will go to temperatures as low as 34°F before taking cold damage. This species is quite drought-tolerant but will grow better if watered regularly during dry periods; however, it should not be overwatered or exposed to excessive moisture levels since this could lead to root rot issues. Pruning should be done regularly to promote new growth and maintain a tidy shape for decorative purposes.
Conclusion:
The mansoa hymenaea is an interesting species that provides multiple benefits for gardeners looking for an attractive yet low-maintenance ornamental vine that can attract wildlife into their gardens while providing them with fragrant flowers throughout the year as well as edible fruits if desired. Growing this garlic vine requires minimal effort but yields great results if given enough sunlight, water, and occasional pruning sessions over time!
The mansoa hymenaea is an interesting species that provides multiple benefits for gardeners looking for an attractive yet low-maintenance ornamental vine that can attract wildlife into their gardens while providing them with fragrant flowers throughout the year as well as edible fruits if desired. Growing this garlic vine requires minimal effort but yields great results if given enough sunlight, water, and occasional pruning sessions over time!
Written by Don Richardson
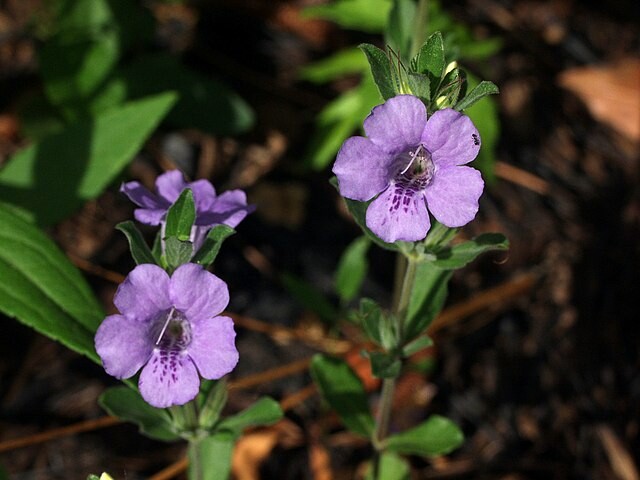
 Swamp Twinflower (Dyschoriste Humistrata)
Swamp Twinflower (Dyschoriste Humistrata)Plant Type | Perennial Groundcover |
Size | 8-20” tall, spreads |
Sun Exposure | Part sun - mostly shade |
Soil Type | loam |
Soil pH | Acidic - Neutral |
Bloom Time | Spring - Fall |
Hardiness Zones | 8a-10a Florida Native |
Moisture | High - moist, can sit in water |
Cold/Heat | 15°F – |
Pollination | Self-pollinates |
Edible Plant | No |
Medicinal Plant | No |
Any reference to medicinal or culinary use of plants or plant parts should in no way be considered an endorsement by The Ocala Food Forest or its staff. Research is crucial in safe and proper consumption or experimentational use of any plant.
Have you ever heard of the Dyschoriste Humistrata, or swamp twinflower? This beautiful and complex plant is native to North America and grows in wetland environments. In this blog post, we will explore the unique characteristics of the swamp twinflower and explain why it has been a source of fascination for botanists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Appearance
The swamp twinflower is an herbaceous perennial and typically grows between 8-20 inches tall. The leaves are lanceolate in shape with serrated edges. The flowers have two petals that are fused together at the base, giving them a 'twin' appearance. The flowers range in color from white to pinkish-purple and bloom during the summer months (June through September).
Habitat & Ecology
Swamp twinflowers prefer wet habitats such as marshes, bogs, streambanks, and riverbanks. They can be found throughout most of the eastern United States and Canada, although they are less common in areas with dryer climates. As a plant that prefers wet environments, it is particularly well adapted for cold climates since it does not need much soil moisture to survive.
The swamp twinflower plays an important role in its environment as a food source for pollinators like bees and butterflies. It also helps stabilize soils near rivers or streams by providing organic material that prevents erosion from fast-moving water. Additionally, its deep root system helps improve water quality by keeping sediment out of waterways while providing oxygenation to aquatic organisms living there.
Conclusion:
The Dyschoriste humistrata is an amazing plant that can be found in wetlands across North America. Its fascinating appearance combined with its ecological importance make it a popular subject among botanists and nature lovers alike. If you’re looking for something interesting to observe on your next outdoor adventure, be sure to keep an eye out for this amazing species!
The Dyschoriste humistrata is an amazing plant that can be found in wetlands across North America. Its fascinating appearance combined with its ecological importance make it a popular subject among botanists and nature lovers alike. If you’re looking for something interesting to observe on your next outdoor adventure, be sure to keep an eye out for this amazing species!
Written by Don Richardson
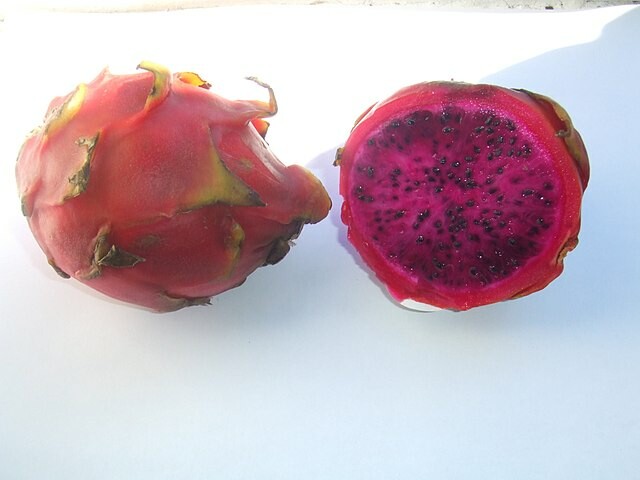
 Dragon Fruit, Red (Hylocereus costaricensis)
Dragon Fruit, Red (Hylocereus costaricensis) Plant Type | Perennial Succulent |
Size | 15-20’ tall, 1’ wide |
Sun Exposure | Full sun - part shade |
Soil Type | Mostly sand |
Soil pH | 6.1-7.5 slightly acidic - Neutral |
Bloom Time | Spring - Fall |
Hardiness Zones | 10-11 Food Forest Plant |
Moisture | Moist–slightly dry well drained |
Cold/Heat | 40°F – 125°F(in part shade) |
Pollination | Needs a pollinator |
Edible Plant | Yes |
Medicinal Plant | Yes |
Any reference to medicinal or culinary use of plants or plant parts should in no way be considered an endorsement by The Ocala Food Forest or its staff. Research is crucial in safe and proper consumption or experimentational use of any plant.
Have you ever seen a dragon fruit plant? Also known as the Hylocereus costaricensis, this unique and beloved plant is native to Central America. It has been grown for centuries in Mexico, Guatemala, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. Its beautiful pinkish-purple flowers and bright yellow-green fruits have made it popular among gardeners and chefs alike. Let’s take a closer look at the dragon fruit plant!
Appearance and Taste
The dragon fruit plant is a cactus that grows on trellises or other structures. It has thick, paddle-like leaves with sharp spines along their edges. The stems can reach up to 20 feet long, with mature plants producing large pinkish-purple flowers that open at night and close during the day. After pollination takes place, these flowers transform into dragon fruits which range in size from two to five inches in length. Dragon fruits come in many varieties that will be different in color. The most common are pink-green on the outside with red pulp inside. They also contain small black edible seeds similar to those found in kiwi fruits. The taste has been described as both tart and sweet with notes of pineapple or kiwi. Again this can be slightly different depending on the variety. Here are a few of the most common.
White pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) has white flesh and pink-red skin. This species includes the Vietnam White, which is the kind you’ll most likely find at the grocery store.
Red pitaya (Hylocereus costaricensis) has the same pink-red skin, but the interior is pinkish-red as well. The coloring ranges from the dark red, dense flesh of the Physical Graffiti variety to the hot pink hue of the red La Verne.
Yellow pitaya (Hylocereus megalanthus) stands out from the others with its bright yellow skin. It has white flesh that, in the Ecuador Palora, is so sweet that it tastes like sugar cubes or honey.
Cultivation of the Hylocereus Costaricensis
In its native Central American habitat, the dragon fruit plant grows wild on trees and shrubs. However, it can also be cultivated in warmer climates such as Mexico or Florida. Dragon fruits also require full sun exposure for optimal growth so they should be planted in an area where they will get plenty of direct sunlight during the day. It should also be kept away from frosty temperatures since this could damage its delicate stems and leaves. They prefer soil with good drainage but need regular watering so that their roots are always moist; however, they should not be overwatered as this can lead to root rot or fungus growth on the stems or leaves of the plant. Additionally, it may need support if its stems become too heavy due to the weight of its fruits.
Uses of Dragon Fruits
Dragon fruits are often eaten fresh but they can also be used in recipes such as smoothies or desserts like ice cream or sorbet. Their mild flavor makes them very versatile in terms of ingredients they can be paired with like tropical fruits like mangoes or pineapples for added sweetness or tart flavors like lime juice for contrast. Additionally, their bright colors make them great for garnishing dishes or decorating platters for special occasions!
Health Benefits
Dragon fruit is a great source of dietary fiber, antioxidants, Vitamin C, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, iron, zinc and other important nutrients. These nutrients help reduce inflammation in the body while also providing essential vitamins and minerals necessary for healthy cells and organs. Additionally, dragon fruit has been found to have anti-aging effects due to its high levels of antioxidants that fight off free radicals that cause cell damage over time. Furthermore, consuming dragon fruit can help lower cholesterol levels due to its high fiber content which helps remove toxins from the body naturally.
Conclusion:
The Hylocereus costaricensis—or dragon fruit plant—is an exotic specimen native to Central America that has been grown commercially for centuries due to its unique beauty and delicious taste! These dragon fruits can then be enjoyed fresh or used in recipes such as smoothies or desserts like ice cream or sorbet! If you’d like to grow your own Hylocereus costaricensis at home, remember to provide it with plenty of direct sunlight and water during dry periods while keeping it away from frosty temperatures so that it thrives!
The Hylocereus costaricensis—or dragon fruit plant—is an exotic specimen native to Central America that has been grown commercially for centuries due to its unique beauty and delicious taste! These dragon fruits can then be enjoyed fresh or used in recipes such as smoothies or desserts like ice cream or sorbet! If you’d like to grow your own Hylocereus costaricensis at home, remember to provide it with plenty of direct sunlight and water during dry periods while keeping it away from frosty temperatures so that it thrives!